What is a list?
College Board Definition: A list is an ordered sequence of elements. The use of lists allows multiple related items to be represented using a single variable.
What does this mean ?
A list is something that holds multiple things in one variable, kinda like a basket holding multiple things.
Whats wrong with this method of data collection?
score1 = 87
score2 = 90
score3 = 85
score4 = 70
score5 = 80
scores = [87, 90, 85, 70, 80]
With list — much easier to loop, modify, and organize
Popcorn Hack 1
What are some possible benefits of using lists? What are some real world examples of lists being used in code ?
Answer
🔍 Click to show answer
Answer: - ✅ Store lots of data in one place - ✅ Access each item individually - ✅ Filter, sort, and organize that dataReal world examples
Without lists, you wouldn’t have:
-
Online Shopping Cart Every time you add an item, it goes into a list. Without a list, you’d only be able to add one item at a time — no checkout with multiple items.
-
Inbox in Email Apps Your inbox is a list of emails. No list? You’d only ever see one email at a time.
-
Music Playlist (Spotify, Apple Music) Every playlist is a list of songs. No list = only 1 song per playlist
Working with Lists
- Creating a List You create a list by placing items inside square brackets [] and separating them with commas. You can store any type of data in a list: strings, numbers, or even other lists.
List1 = ["Ford", "Ferrari", 1922]
List2 = ["BMW", "Honda", List1]
print(List2)
['BMW', 'Honda', ['Ford', 'Ferrari', 1922]]
- Accessing List Elements
- You can access any element in the list by using its index. The index starts at 0 for the first element.
cars = ["Jaguar", "Ford", "Kia"]
print(cars[0]) # Output: apple
print(cars[1]) # Output: banana
Jaguar
Ford
- Modifying List Elements Lists are mutable, meaning you can modify an element by referring to its index and assigning it a new value.
cars[1] = "Rivian"
print(cars)
['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry']
- Adding Elements to a List
- You can add elements to a list in two main ways:
- append(): Adds an item to the end of the list.
- insert(index, item): Adds an item at a specific position in the list.
# Append a new fruit to the end
cars.append("BMW")
print(cars) # Output: ['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry', 'mango']
# Insert a car at the second position
cars.insert(1, "Mazda")
print(cars)
['Jaguar', 'Ford', 'Kia', 'BMW']
['Jaguar', 'Mazda', 'Ford', 'Kia', 'BMW']
- Removing Elements from a list
animals = ["cat", "dog", "fish"]
animals.pop(1) # removes "dog"
print(animals)
['cat', 'fish']
- Slicing up a list
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
first_five = numbers[0:5]
print(first_five)
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
📋 Common List Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| append(item) | Adds an item to the end of the list | scores.append(100) |
| insert(index, item) | Inserts an item at a specific position | scores.insert(1, 95) |
| remove(item) | Removes the first matching item | scores.remove(87) |
| pop(index) | Removes and returns the item at the given index | scores.pop(2) |
| len(list) | Returns the number of items in the list | len(scores) |
| slice[start:end] | Returns a portion of the list | scores[0:3] |
| sort() | Sorts the list in ascending order | scores.sort() |
| reverse() | Reverses the order of the list | scores.reverse() |
| clear() | Removes all elements from the list | scores.clear() |
| index(item) | Returns the index of the first matching item | scores.index(90) |
Popcorn Hack 2
What does this code output?
items = ["pen", "pencil", "marker", "eraser"]
items.remove("pencil")
items.append("sharpener")
print(items[2])
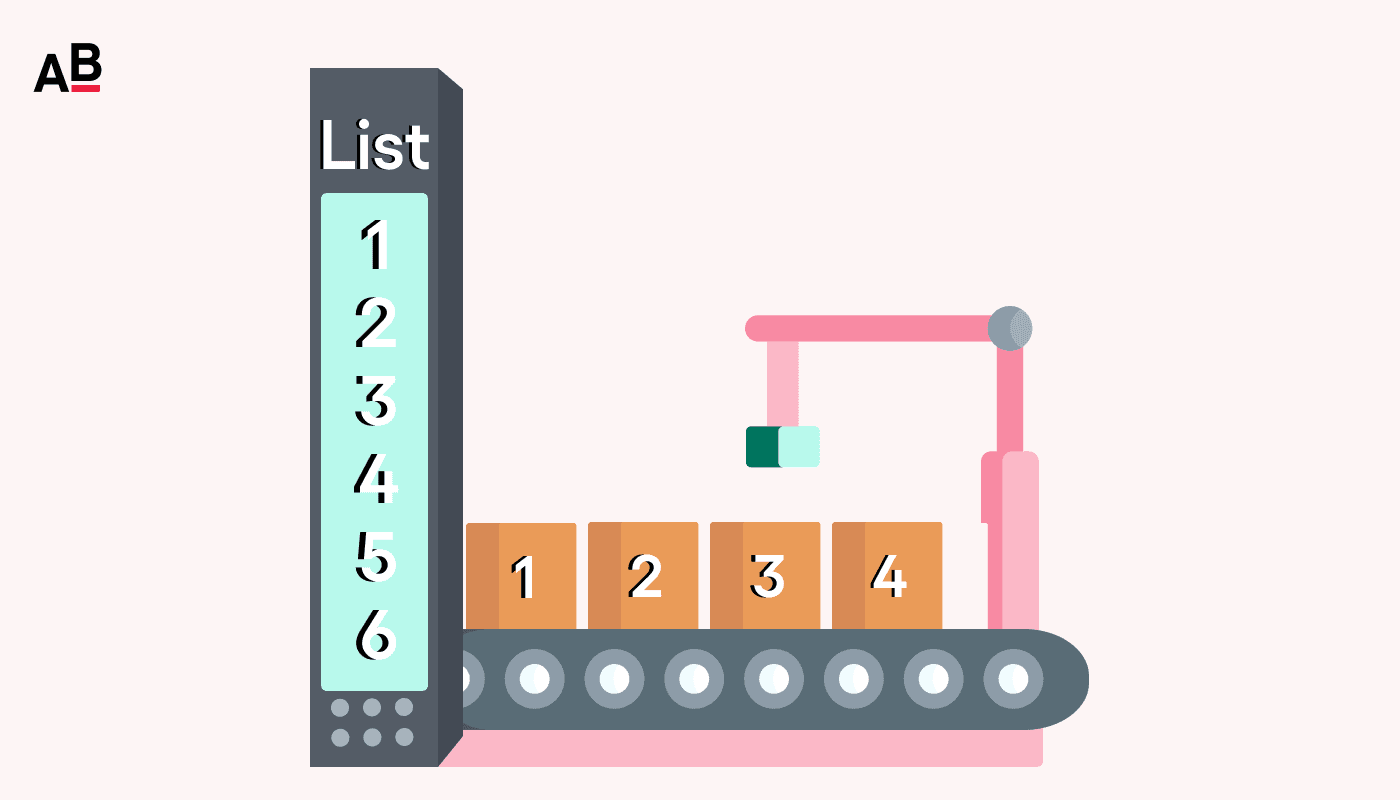
Traversing a List

College Board requires that students know how to traverse a list.
Traversing a list means going through each item one by one using a loop. Traversing lists are a key factor in creating filtering algorithms.
colors = ["red", "blue", "green", "yellow"]
for color in colors:
print("Color:", color)
Real life Examples:
- 📧 Emails - Check each email and mark unread ones
- 🎮 Game Scores - Add all scores to find the total
- 🛍️ Shopping - Find cheapest item
- 📊 Data Analysis - Count how many items meet a condition
Traversal List with Conditions
grades = [85, 92, 76, 98, 88]
above_90 = []
for grade in grades:
if grade > 90:
above_90.append(grade)
print("Grades above 90:", above_90)
# Using iteration + selection (if statement) to create a filtered list.
Grades above 90: [92, 98]
Why do we need to know about lists for AP CSP?
📌 Lists are needed for...
✅ College Board requires the use of lists for the Create Performance Task .
✅ Lists are also part of Big Idea 3 in the AP CSP curriculum (Section 3.10) and will appear on the MCQ.

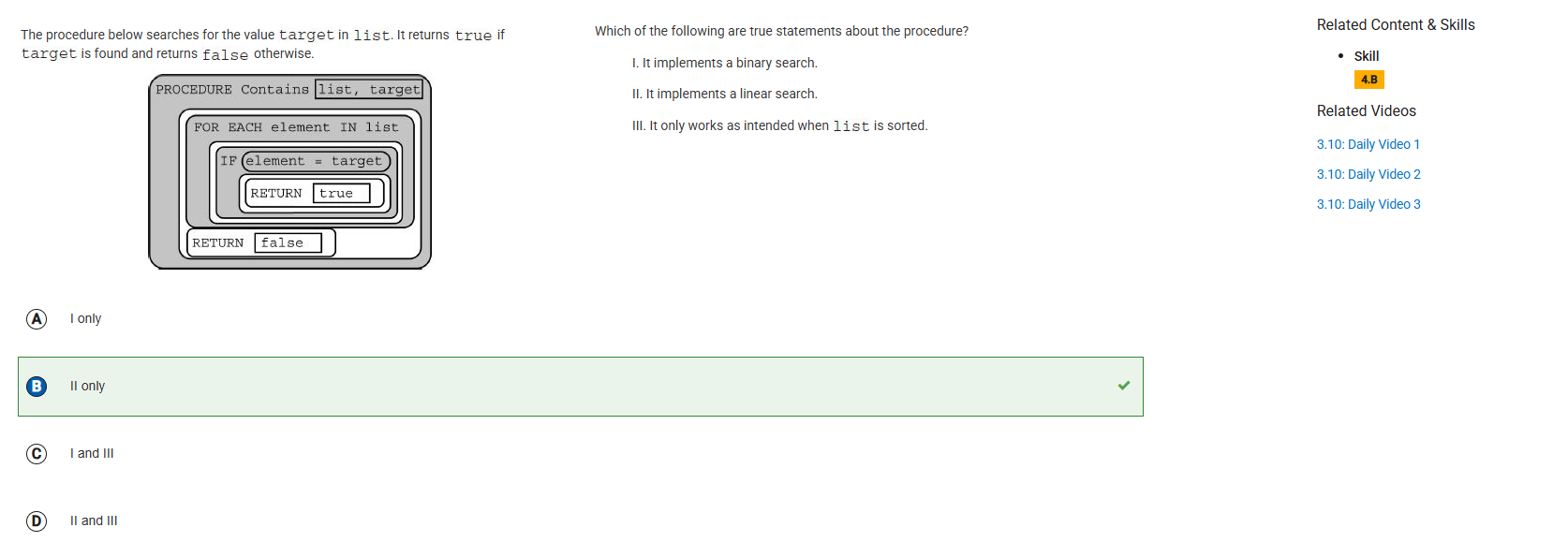
Example College Board question
Filtering Algorithim
College Board states that an algorithim is “a finite set of instructions that accomplish a specific task.” They also say that “Filtering algorithms are important tools for finding information and recognizing patterns in data.”
So what are they?
In basic terms:
- 🔍 Filtering algorithm:
- Loops through the list (TRAVERSAL LIST!)
- Checks a condition
- Stores matching items in a new list.

Example of a filtering algorithm
numbers = [3, 8, 12, 5, 7, 14]
even_numbers = []
for num in numbers:
if num % 2 == 0:
even_numbers.append(num)
print(even_numbers)
[8, 12, 14]
Start with a list: numbers = [3, 8, 12, 5, 7, 14]
Traverse the list using a for loop.
Apply a condition: if num % 2 == 0 (check if the number is even)
Build a new list: even_numbers only contains items that meet the condition.
# List of names
names = ["Keerthan", "Zafeer", "Hitin"]
# Get user input
search = input("Type part of a name to search: ").lower()
# Create a filtered list
filtered_names = []
for name in names:
if name.lower().startswith(search):
filtered_names.append(name)
# Show results
print("Filtered names:", filtered_names)
Filtered names: ['Zafeer']
Original list: names = [“Keerthan”, “Zafeer”, “Hitin”]
User input: The user types part of a name (like “K”).
Traversal List: It loops through every name in the list
Condition: It checks if each name starts with the user input.
Filtering: It builds a new list of names that match.
Popcorn Hack 3: What are some real world examples of filtering algorithms?
🔍 Click to show answer
- 📧 Inbox → email is unread → Unread emails only (new list)
- 🛒 Online Shopping → price < $20 → Discounted items (new list)
- 🎵 Spotify → Artist == "Singer A" → Only songs by Singer A (new list)
✅ Goes through a list 🔎 Checks for a match 📤 Returns only the things that pass the test in a NEW list
How does it relate to Flask Projects?
- Can filter through a database.
- A user types in a specific filter (what they are looking for)
- Flask filters matching items from a backend database (e.g. SQL)
- Flask uses jsonify to return the filtered list to the frontend
Additional Resources
Homework Hacks (Create Notebook file to run python code)
Instructions:
1) Create a list that includes at least five items
Use at least three different list procedures:
Label with comments where each list procedure is used and explain what it’s doing.
2) List Traversal Instructions:
Write the steps for how you would go through your list one item at a time.
Clearly describe how the traversal happens (loop type and structure).
3) Filtering Algorithm (Use pandas - database filtering) Instructions:
- Choose a condition
- Write out the steps you would take to:
- Start with a list
- Go through each item (traversal)
- Apply your condition
Build a new list with only the items that pass your test
✏️ Final Reflection (2 Sentences) Answer this:
In two complete sentences, explain when and how filtering algorithms and lists are used in real life.